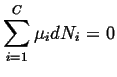 |
(20-17) |
The simple expression for the chemical potentials in an ideal gas can be put into the equilibrium condition:
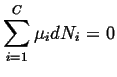 |
(20-17) |
and equilibrium amounts of material can be calculated.
If we have a closed system (fixed number of moles of the independent species), then
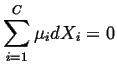 |
(20-18) |
A Simple Example
Consider the gaseous reaction
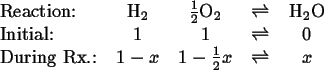
Therefore,
![]() and
and
![]() (Every mole of hydrogen gas that appears is associated
with the disappearance of one mole of water vapor;
every mole of water vapar that appears is associated
with the disappearance of one half a mole of oxygen gas).
(Every mole of hydrogen gas that appears is associated
with the disappearance of one mole of water vapor;
every mole of water vapar that appears is associated
with the disappearance of one half a mole of oxygen gas).
Therefore, the condition for equilibrium (Equation 20-18) for an ideal gas mixture becomes:
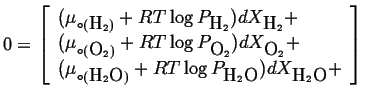 |
(20-19) |
which is possible only if
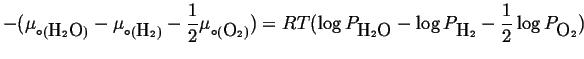 |
(20-20) |
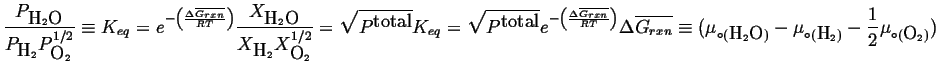 |
(20-21) |
In general for ideal gas mixture with reaction
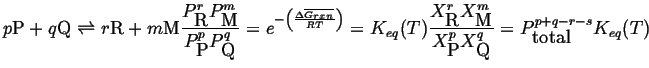 |
(20-22) |
where the molar free energy change of the reaction is:
and generalizing even more
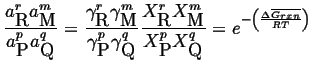 |
(20-23) |