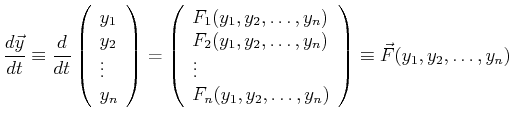 |
(24-12) |
The critical point plays a very important role in understanding the behavior of non-linear ODEs.
The general autonomous non-linear ODE can be written as:
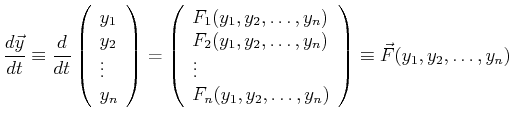 |
(24-12) |
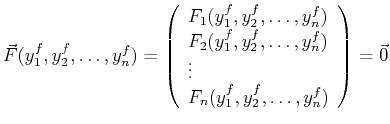 |
(24-13) |
| (24-16) |
Rather than solve the matrix equation directly, it makes more
sense to transform the system into one that is diagonalized.
In other words, instead of solving
Eq. 24-14 with
Eq. 24-15 near the fixed point,
find the eigenvalues, ![]() , of Eq. 24-15 and
solve the simpler system by transforming the
, of Eq. 24-15 and
solve the simpler system by transforming the
![]() into
the eigenframe
into
the eigenframe
![]() :
:
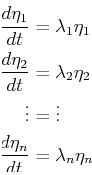 |
(24-17) |
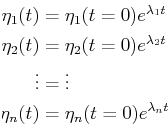 |
(24-18) |
If any of the eigenvalues of ![]() are positive, then
an initial condition near that fixed point will diverge from
that point--stability occurs only if all the eigenvalues are
negative.
are positive, then
an initial condition near that fixed point will diverge from
that point--stability occurs only if all the eigenvalues are
negative.
|
MATHEMATICA |
| (notebook Lecture-24) |
| (html Lecture-24) |
| (xml+mathml Lecture-24) |
| Analyzing Stability for the Predator-Prey Problem
|