- ... state.1
-
Recall from the simulations in class that the particle spends most of its time
in the well and most of the rest of its time near the saddle points where the
net velocity is small.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... state:2
-
This is certainly important for the case for migrating particles that have
a large compliance (low stiffness) such as vacancies.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... independently:3
-
Note that
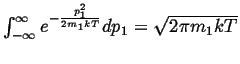 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... parts4
- The boundary conditions may be chosen to
make the "
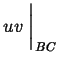 " part vanish, or the surface term may
be considered to be small compared to the volume.
" part vanish, or the surface term may
be considered to be small compared to the volume.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
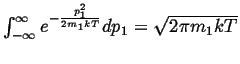 .
.
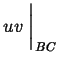 " part vanish, or the surface term may
be considered to be small compared to the volume.
" part vanish, or the surface term may
be considered to be small compared to the volume.